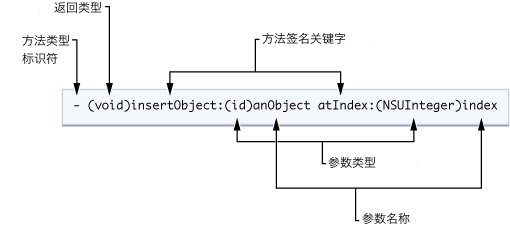
Objective-C 类
介绍
在 OC 中使用 @interface 关键字声明一个类:
@interface MyClass : NSObject
{
int count;
id data;
NSString* name;
}
- (id)initWithString:(NSString*)aName;
+ (MyClass*)myClassWithString:(NSString*)aName;
@end
实现类:
#import "Student.h"
@implementation Student
-(void) printInfo
{
NSLog(@"姓名:%@ 年龄:%d岁",studentName,studentAge);
}
-(void) setStudentName: (NSString*) name
{
studentName = name;
}
@end
创建一个类
在 XCode 中,File - New - File,选择 Cocoa,选择 Objective-C 类。类名输入 BNRPerson,继承自 NSObject。
项目中将会创建两个文件 BNRPerson.m 和 BNRPerson.h。在 BNRPerson.h 中,包含两个成员变量:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface BNRPerson : NSObject
{
float _heightInMeters;
int _weightInKilos;
}
- (float)heightInMeters;
- (void)setHeightInMeters:(float)h;
- (int)weightInKilos;
- (void)setWeightInKilos:(int)w;
- (float)bodyMassIndex;
@end
头文件以 @interface 开始,以 @end 结尾。用下划线表示是否是私有成员。成员定义在花括号里,紧跟着是类方法。
在头文件和实现文件中切换的快捷键:Control-Command-up
BNRPerson.m 类实现:
#import "BNRPerson.h"
@implementation BNRPerson
- (float)heightInMeters
{
return _heightInMeters;
}
- (void)setHeightInMeters:(float)h
{
_heightInMeters = h;
}
- (int)weightInKilos
{
return _weightInKilos;
}
- (void)setWeightInKilos:(int)w
{
_weightInKilos = w;
}
- (float)bodyMassIndex
{
return _weightInKilos / (_heightInMeters * _heightInMeters);
}
@end
这里的访问方法可以通过 properties 特性省略掉。
类方法
在 Objective-C 中,调用类方法,实际上是像这个类的实例发出一个调用方法的消息。
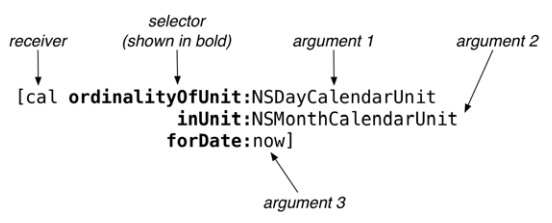
消息使用方括号修饰,由两个部分组成:
- 接收者(receiver)
- 选择器(selector)
例如:
NSDate *now = [NSDate date];
其中:
- NSDate 是接收者,拥有这个方法的类或对象
- date 是选择器,指定要运行哪个方法
类方法怎么看:
类方法和实例方法
也就是静态方法和实例方法。
带参数的消息
单个参数示例:
[now dateByAddingTimeInterval:100000];
多个参数示例:
[cal ordinalityOfUnit:NSDayCalendarUnit
inUnit:NSMonthCalendarUnit
forDate:now];
参数分析:
这个方法包含 3 个参数,方法名分成 3 个部分,但这是一个消息,触发了一个方法。
A of B,这句话,inUnit 表示 B, ordinalityOfUnit 表示 A, forDate 表示被计算的对象。
嵌套消息发送
[[NSDate date] timeIntervalSince1970];
向 nil 发送消息
在 Objective-C 中不使用 NULL,而是用 nil,nil 表示不指向任何对象,都表示 zero 指针。
在 Objective-C 的设计中,允许向 nil 发送消息,结果只不过是什么都不发生。
alloc 和 init
alloc 用于创建类实例,返回指向新实例的指针。
此时这个实例还需要被初始化。未被初始化的实例,尽管内存分配了,但是还没有准备好接收消息。
init 方法用于对实例进行初始化。
这两个方法通常嵌套使用:
[[NSDate alloc] init];
类成员
可访问性
不指定默认都是 protected 的。
@interface Worker : NSObject
{
char *name;
@private
int age;
char *evaluation;
@protected
id job;
float wage;
@public
id boss;
}
创建类实例
Student *student = [[Student alloc]init];
[student setStudentName:@"张三"];
[student setAge:10];
[student printInfo];
[student release];
类属性
在 Objective-C 中,有一种名为属性(properties)的特性,能省掉声明实例变量,省掉实现访问方法。
实例代码如下:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface BNRPerson : NSObject
// 没有中括号了
@property (nonatomic) float heightInMeters;
@property (nonatomic) int weightInKilos;
……
@end
properties attributes
nonatomic 和 atomic
两个里面选择一个,与多线程相关。
readonly 和 readwrite
readonly 属性只读:
@property (nonatomic, readonly) double circumferenceOfEarth;
编译器只会创建 getter,但是不会创建 setter。 readwrite 可读可写:
@property (nonatomic, readwrite) double humanPopulation;
默认就是 readwrite,因此可以不写。
点语法
property 创建的 getter 和 setter 可以通过点语法进行访问:
mikey.weightInKilos = 96;
int weight = mikey.weightInKilos;
需要注意的是,点其实还是对 getter 和 setter 的方法调用,还会发送消息。
id
在很多时候需要创建一个指针,但是不知道它的具体类型是什么。这种情况下使用 id 类型,表示指向某种 Objective-C 对象的指针:
id delegate;